Display Title
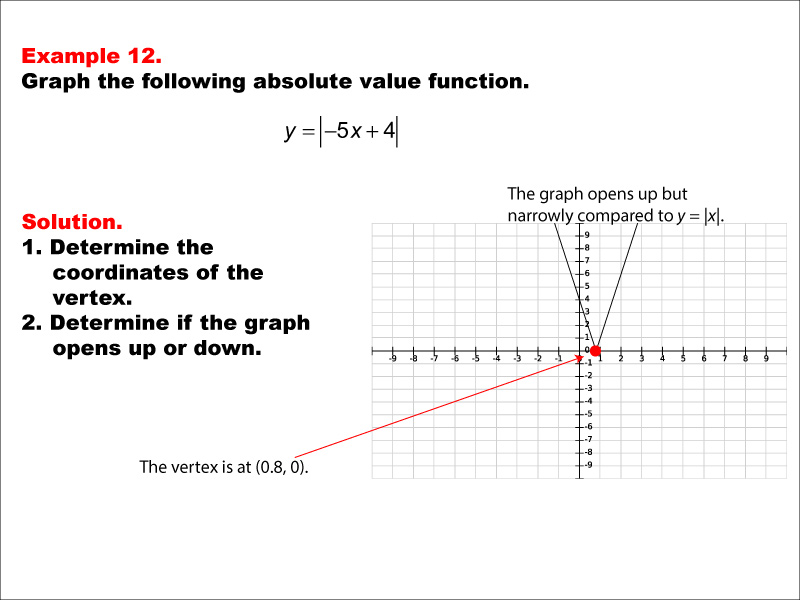
Math Example: Absolute Value Functions: Example 12
Display Title
Math Example: Absolute Value Functions: Example 12
Math Example: Absolute Value Functions: Example 12
This is part of a collection of math examples that explore different properties of absolute value. From comparing absolute values of different numerical expressions to different representations of absolute value functions, this collection provides a wide array of examples.
To see the complete math example collection on this topic, click on this link.
Note: The download is an image file.
Related Resources
To see additional resources on this topic, click on the Related Resources tab.
Create a Slide Show
Subscribers can use Slide Show Creator to create a slide show from the complete collection of math examples on this topic. To learn more about Slide Show Creator, click on this Link:
Accessibility
This resource can also be used with a screen reader. Follow these steps.
-
Click on the Accessibility icon on the upper-right part of the screen.

-
From the menu, click on the Screen Reader button. Then close the Accessibility menu.

-
Click on the PREVIEW button on the left and then click on the definition card. The Screen Reader will read the definition.
| Common Core Standards | CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSF.IF.C.7.B |
|---|---|
| Grade Range | 6 - 12 |
| Curriculum Nodes |
Algebra • Functions and Relations • Special Functions |
| Copyright Year | 2013 |
| Keywords | function, graph, vertex, vertices |