Display Title
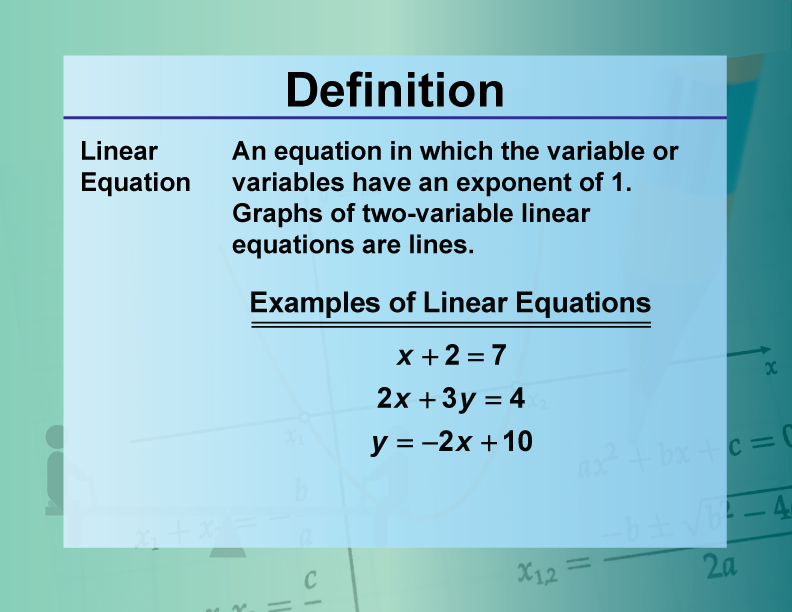
Definition--Equation Concepts--Linear Equation
Display Title
Definition | Equation Concepts | Linear Equation
This is a collection of definitions related to equations and similar topics. This includes general definitions for equations, as well as terms related to parts of an equation, different types of equations, and characteristics of equations.
—PRESS PREVIEW TO SEE THE DEFINITION—
To see the complete collection of definitions, click on this link.
The following section provides additional information on solving one- and two-step equations.
Solving One-Step Equations
A one-step equation can literally be solved in one step. This is because the equation is written in a form such that an inverse operation is enough to solve it. Here are the different forms a one-step equation can take:
|
Equation Type |
Inverse Operation |
Example |
|
Addition |
Subtraction |
|
|
Subtraction |
Addition |
|
|
Multiplication |
Division |
|
|
Division |
Multiplication |
|
With these four basic cases, there are a number of variations, depending on the numbers involved. The simplest types of these equations involve positive whole numbers. But these equations can involve integers and rational numbers.
The general form of each of the four types of basic one-step equations are summarized here.
Solving Two-Step Equations
You saw that with one-step equations, the “one step” involved one inverse operation. With two-step equations, there are two inverse operations involved in solving the equation. But this extra step introduces many more types of equations to solve, beyond the basic four from one-step equations.
There are 16 basic types of two-step equations that involve different combinations of the four basic operations.
|
|
Addition |
Subtraction |
Multiplication |
Division |
|
Addition |
AA |
AS |
AM |
AD |
|
Subtraction |
SA |
SS |
SM |
SD |
|
Multiplication |
MA |
MS |
MM |
MD |
|
Division |
DA |
DS |
DM |
DD |
These 16 basic examples are summarized in the table below, where we show an example of such an equation using numbers, then followed by a general form of the equation using variables and constant terms.
|
Equation Type |
Inverse Operations |
Example |
General Form |
|
Addition and Addition |
Subtraction and Subtraction |
|
|
|
Addition and Subtraction |
Subtraction and Addition |
|
|
|
Addition and Multiplication |
Subtraction and Division |
|
|
|
Addition and Division |
Subtraction and Multiplication |
|
|
|
Subtraction and Addition |
Addition and Subtraction |
|
|
|
Subtraction and Subtraction |
Addition and Addition |
|
|
|
Subtraction and Multiplication |
Addition and Division |
|
|
|
Subtraction and Division |
Addition and Multiplication |
|
|
|
Multiplication and Addition |
Division and Subtraction |
|
|
|
Multiplication and Subtraction |
Division and Addition |
|
|
|
Multiplication and Multiplication |
Division and Division |
|
|
|
Multiplication and Division |
Division and Multiplication |
|
|
|
Division and Addition |
Multiplication and Subtraction |
|
|
|
Division and Subtraction |
Multiplication and Addition |
|
|
|
Division and Multiplication |
Multiplication and Division |
|
|
|
Division and Division |
Multiplication and Multiplication |
|
|
These 16 basic two-step equations come in different forms depending on the sign of the numbers and whether the numbers are integers or rational numbers. The simplest types of these equations involve positive whole numbers.
|
Equation Type |
General Form |
|
Addition |
|
|
Subtraction |
|
|
Multiplication |
|
|
Division |
|
Note: The download is a PNG file.
Related Resources
To see additional resources on this topic, click on the Related Resources tab.
Create a Slide Show
Subscribers can use Slide Show Creator to create a slide show from the complete collection of math definitions on this topic. To see the complete collection of definitions, click on this Link.
To learn more about Slide Show Creator, click on this Link.
Accessibility
This resources can also be used with a screen reader. Follow these steps.
-
Click on the Accessibility icon on the upper-right part of the screen.

-
From the menu, click on the Screen Reader button. Then close the Accessibility menu.

-
Click on the PREVIEW button on the left and then click on the definition card. The Screen Reader will read the definition.
| Common Core Standards | CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.6.EE.B.5, CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.EE.B.4, CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSA.REI.A.1 |
|---|---|
| Grade Range | 6 - 12 |
| Curriculum Nodes |
Algebra • Linear Functions and Equations • Applications of Linear Functions |
| Copyright Year | 2021 |
| Keywords | equations, solving equations, definitions, glossary terms |